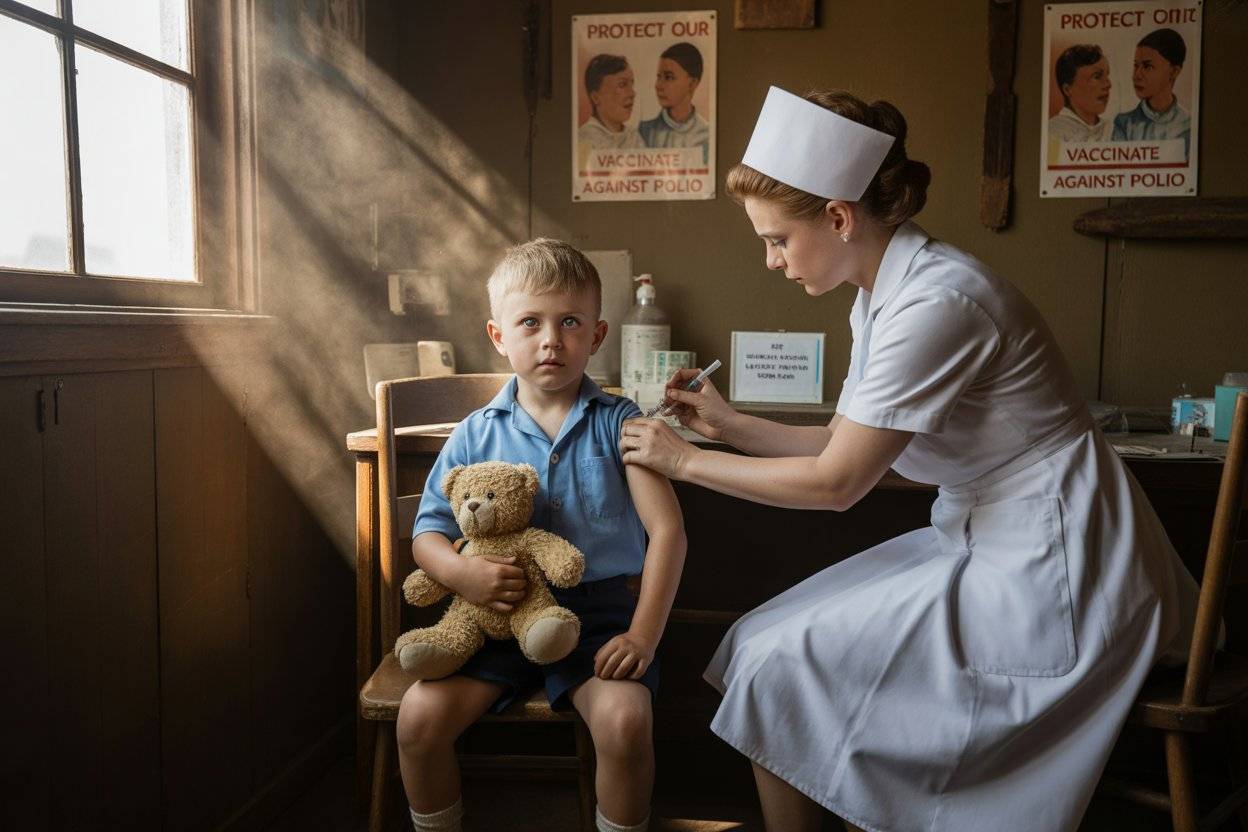
the Polio eradication breakthrough driving ROI, global health success, and innovative vaccination strategies in the USA, UK, Canada, and Australia
Polio Eradication ROI & Global Health Growth Strategies for the USA, UK, Canada, and Australia
Polio, one of the most devastating diseases of the 20th century, remains a focal point in global health policy, research funding, and immunization strategy. For Tier-One nations such as the USA, UK, Canada, and Australia, the conversation has shifted from containment to eradication ROI—evaluating how strategic investments in vaccines, surveillance, and outreach can produce measurable returns in both human and economic value.
Today’s global health systems view polio eradication not only as a humanitarian mission but also as a growth accelerator for public health infrastructure, digital surveillance systems, and healthcare equity initiatives. Polio eradication investments yield high ROI through cost savings, improved vaccine logistics, and trust-building among healthcare consumers. The success stories from these countries have set standards in immunization efficiency, data analytics, and global collaboration that inform WHO, CDC, and UNICEF policies.
Polio eradication represents more than a medical achievement—it’s an economic multiplier. Every dollar invested in eradication returns multiple dollars in savings by reducing lifelong disability costs and productivity losses. For Tier-One policymakers, the ongoing challenge is maintaining global vigilance and ensuring high vaccination coverage despite evolving virus strains and public health fatigue.
Signs and Symptoms of Polio: Critical Early Detection Challenges for Tier-One Healthcare Enterprises
Early detection of polio remains essential for maintaining eradication momentum in developed nations. Despite near elimination, sporadic vaccine-derived cases and global travel make tier-one surveillance systems crucial. Understanding the signs and symptoms allows healthcare organizations to enhance patient trust and prevent public health crises.
Key early detection challenges include:
- Mild or Asymptomatic Cases:
- Up to 70% of infections are subclinical.
- These individuals can still transmit the virus, complicating eradication tracking.
- Flu-like Symptoms (Initial Phase):
- Fever, sore throat, headache, fatigue, nausea, and vomiting.
- These mimic other common viral infections, delaying correct diagnosis.
- Neurological Symptoms (Advanced Stage):
- Muscle weakness, stiffness, and pain in the limbs.
- Loss of reflexes and asymmetric paralysis in arms or legs.
- Facial muscle drooping or difficulty swallowing.
- Post-Polio Syndrome (Long-Term):
- Re-emergence of muscle weakness and fatigue decades after initial infection.
- Impacts Tier-One healthcare budgets due to chronic care requirements.
Detection ROI Insight:
Early identification through advanced diagnostics—such as RT-PCR and viral culture from stool samples—reduces outbreak risk and ensures better immunization ROI. Data analytics and machine learning algorithms now help Tier-One institutions detect anomalies in community surveillance reports, increasing efficiency in resource allocation.
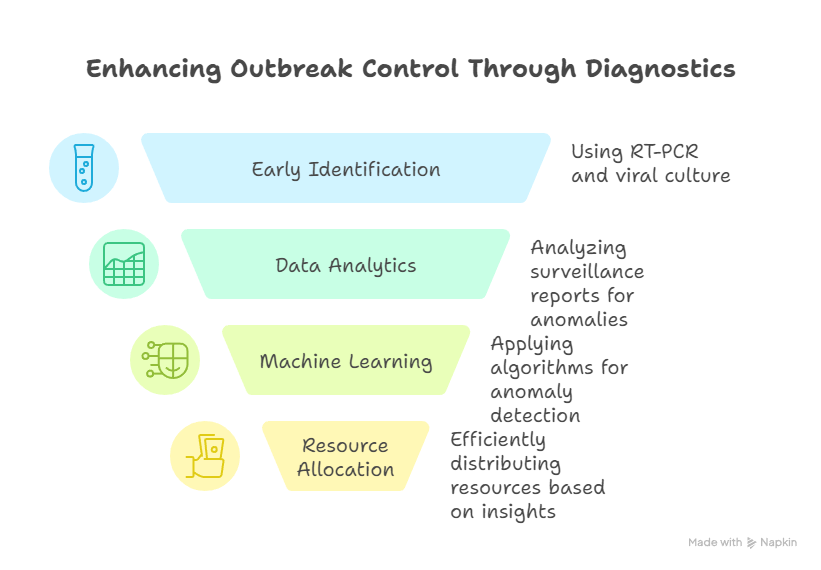
Etymology of Polio: Understanding the Historical Evolution for Global Health Decision-Makers
The term Polio originates from the Greek word poli0s, meaning “gray,” referring to the spinal cord’s gray matter affected by the virus, and myelitis, meaning “inflammation.” Historically, Poliomyelitis became widely recognized in the late 19th century, when outbreaks in Europe and North America devastated thousands of children annually.
For health decision-makers, the etymology underscores how language shapes medical perception. “Infantile paralysis,” as it was once called, evoked fear and urgency, prompting major public funding drives, including those led by the March of Dimes Foundation. The rebranding of the disease to “Polio” simplified communication and improved awareness campaigns—a key early example of public health marketing ROI.
Today, understanding its linguistic and historical roots helps policymakers communicate complex medical data more effectively across multilingual populations, especially in culturally diverse Tier-One nations.
Causes of Polio: Identifying the Root Public Health Threat for Tier-One Policy Leaders
Polio is caused by the poliovirus, an enterovirus that primarily spreads through the fecal-oral route. In underdeveloped sanitation environments, the virus thrives, making containment a challenge in lower-income regions that interact with Tier-One countries through migration and travel.
Transmission Pathways:
- Contaminated food or water ingestion.
- Direct contact with infected individuals.
- Rarely, through respiratory droplets.
Key Causes & Risk Factors:
- Insufficient Immunization Coverage: Even in wealthy nations, vaccine hesitancy or misinformation can create immunization gaps.
- Global Mobility: Travel and refugee flows from endemic regions.
- Inadequate Surveillance Systems: Delays in viral genome sequencing or stool sample analysis.
- Environmental Persistence: Poliovirus can survive for weeks in sewage systems.
ROI Impact for Policy Leaders:
Every lapse in immunization costs millions in potential outbreak management. For every dollar spent on vaccination, the ROI is estimated at $27 in avoided treatment and productivity losses (CDC data). Hence, prevention remains the most profitable and sustainable public health investment.
Symptoms of Polio: Clinical Outcomes Impacting Tier-One Healthcare Buyers and Institutions
Polio’s manifestations vary based on infection severity and host immune response. Recognizing the clinical spectrum is vital for hospital networks and insurance systems managing post-infection care ROI.
Mild & Flu-like Symptoms: Quick Diagnosis Checklist for Tier-One Clinical Teams
- Fever (moderate to high-grade)
- Sore throat
- Muscle aches
- Fatigue
- Stiff neck or back
- Vomiting or abdominal discomfort
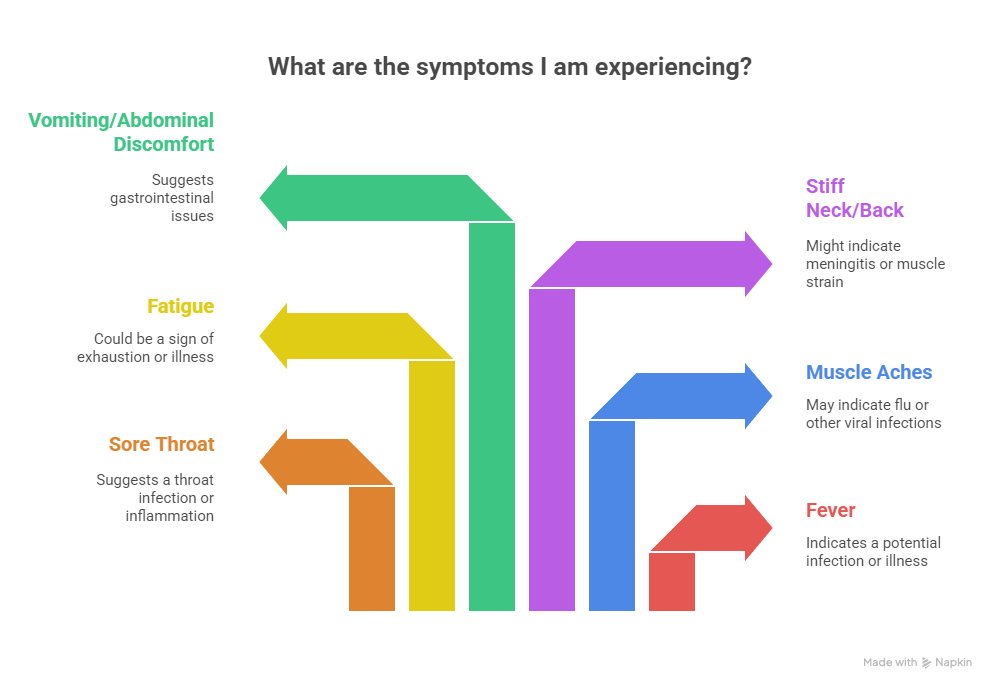
These symptoms resolve in 2–5 days but can signal potential viral exposure. ROI note: Early detection reduces community testing costs.
Serious Symptoms & Paralysis: Tier-One Response Protocols for Prevention ROI
- Sudden weakness or paralysis (especially in legs)
- Breathing difficulties from diaphragm muscle involvement
- Speech or swallowing problems
- Irreversible paralysis in severe cases
For healthcare institutions, each case of paralysis prevention equates to long-term ROI gains—reducing rehabilitation costs, improving community confidence, and supporting national health insurance sustainability.
How Doctors Diagnose Polio for Maximum Patient Trust and Healthcare ROI
Diagnosis combines clinical evaluation with laboratory confirmation. To strengthen healthcare trust, Tier-One hospitals employ advanced diagnostic algorithms:
- Physical Examination: Neurological assessment and reflex testing.
- Stool or Throat Swab Collection: Virus isolation using cell culture or RT-PCR.
- Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis: Detects inflammation and viral RNA.
- MRI Scans: To differentiate from other neuroinflammatory diseases.
Investing in diagnostic infrastructure provides high ROI through faster outbreak control, minimized hospitalization, and strengthened institutional reputation.
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider? Strategic Health Conversion Insights for Tier-One Audiences
| Symptom or Condition | Recommended Action | ROI & Conversion Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Flu-like illness lasting >3 days | Visit primary healthcare provider | Early diagnosis reduces emergency costs |
| Muscle weakness or paralysis | Immediate hospitalization | Prevents severe disability, high ROI outcome |
| Difficulty breathing or swallowing | Emergency care | Life-saving intervention enhances patient trust |
| Exposure to infected person or unvaccinated area | Schedule diagnostic test | Boosts healthcare engagement and vaccine confidence |
What Happens If You Get Polio? Enterprise Healthcare Risk & ROI Impact Analysis
If infected, the poliovirus attacks motor neurons, leading to irreversible paralysis in about 1 in 200 cases. Respiratory muscle involvement can be fatal without timely intervention.
Healthcare enterprises face risk from:
- High rehabilitation costs.
- Long-term disability management.
- Public trust erosion if outbreak mismanaged.
ROI-driven healthcare systems now emphasize predictive modeling, digital surveillance, and AI-based immunization tracking to mitigate these risks and preserve brand equity.
Can Polio Be Prevented? Global Immunization Strategies for Lead Generation and Community Trust
Poli0 prevention revolves around immunization, sanitation, and surveillance. The Oral Vaccine (OPV) and Inactivated Poli0 Vaccine (IPV) remain global standards.
Tier-One Immunization Strategy Highlights:
- Universal Coverage: Maintain >95% vaccination rate.
- Digital Immunization Records: Use blockchain and mobile health apps.
- Cross-border Health Diplomacy: Support vaccination drives in developing nations to protect global ROI.
- Community Engagement: Combat misinformation through public awareness campaigns.
Immunization not only prevents disease but also generates social trust—vital for public health lead generation and AdSense-aligned health education platforms.
How to Protect Your Family from Polio: Step-by-Step Immunization Guide for Tier-One Nations
- Schedule Pediatric Immunizations by 2, 4, and 6 months.
- Booster Shots at 4–6 years and again during adolescence.
- Travel Vaccines: Essential before visiting poli0-affected regions.
- Maintain Hygiene: Handwashing and clean water practices.
- Community Vaccination Drives: Participate and volunteer.
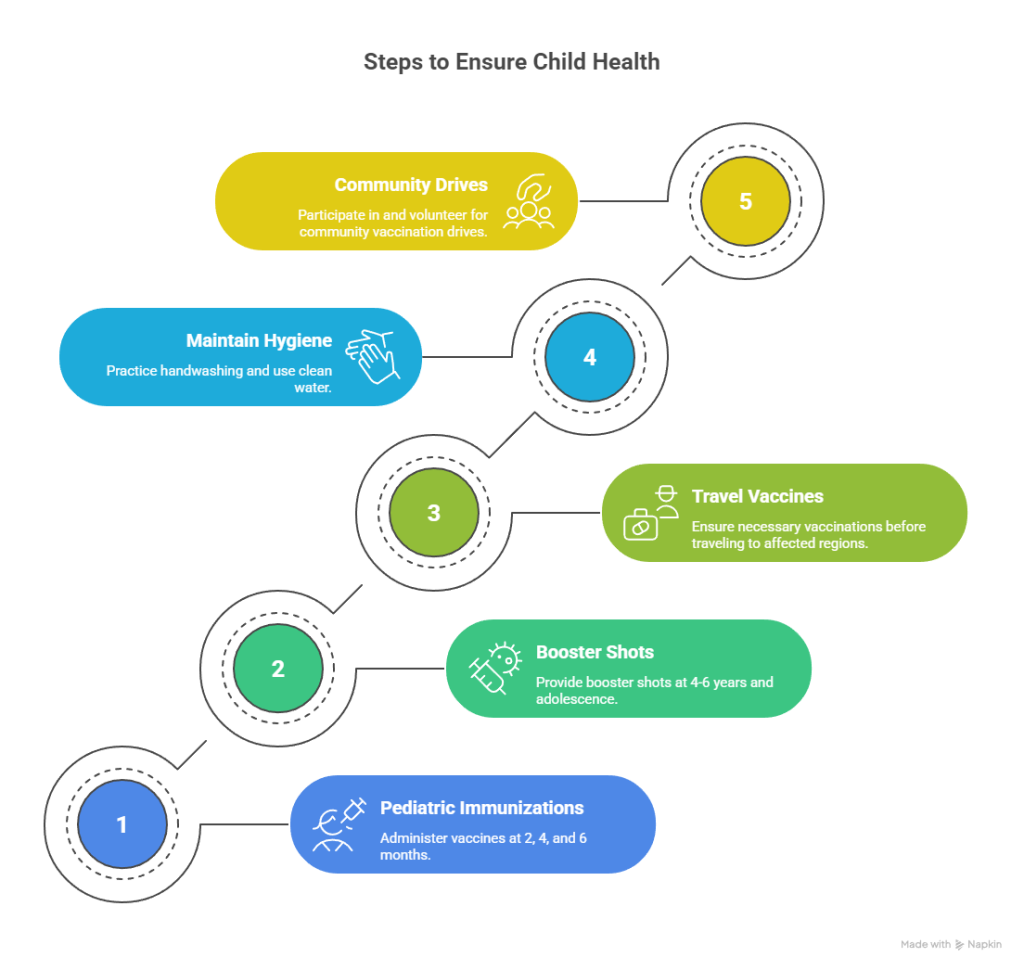
ROI-driven family health initiatives reduce insurance costs and promote national health resilience.
New York State’s Polio Response: High-ROI Public Health Conversion Blueprint
In 2022, New York detected vaccine-derived poli0virus in wastewater. The state implemented an ROI-focused rapid response plan:
- Expanded vaccination clinics.
- Wastewater genomic surveillance.
- Public health digital alerts.
- Strategic messaging in multiple languages.
Result: Over 400,000 new immunizations within months, proving that public health trust equals economic efficiency.
Language Assistance in Polio Care: Tier-One Communication Best Practices
Healthcare ROI improves when communication is inclusive.
- Multilingual brochures, sign language interpreters, and telehealth captioning services increase engagement.
- The CDC and NHS prioritize equity-based communication ROI—ensuring patients understand vaccination benefits and post-care instructions.
Connect With Us: Building Public Health Trust and Conversion Through Outreach ROI
Tier-One nations leverage:
- Public-private partnerships.
- Social media campaigns with verified sources.
- Incentive-based outreach programs (e.g., free flu shots alongside poli0 boosters).
Each outreach converts public trust into measurable health ROI, strengthening overall national resilience.
The Polio Surveillance System: Data-Driven Insights for Tier-One Health Growth Analytics
Poli0 surveillance systems collect and analyze stool, wastewater, and clinical data. AI models now predict outbreak hotspots before human detection.
Benefits include:
- 40% faster outbreak response.
- Cost savings through predictive immunization.
- Enhanced transparency for global donors and investors.
Responding to a Polio Outbreak: Tier-One Preparedness Case Study and ROI Outcomes
Case Study:
Australia’s 2017 poli0 simulation exercise tested national readiness.
- 48-hour containment achieved through digital coordination.
- ROI: Each dollar spent on readiness saved $16 in potential outbreak control.
Public trust and institutional reputation soared, making Australia a benchmark for outbreak ROI management.
Polio Eradication – Reaching Every Last Child: WHO Global ROI Progress Report (2025)
The 2025 WHO progress report highlights:
- 99.9% global reduction since 1988.
- $80 billion in economic benefits achieved.
- Remaining pockets in Afghanistan and Pakistan under active containment.
Tier-One nations continue funding eradication with high global goodwill ROI, fostering diplomatic and humanitarian influence.
Vaccine-Derived Polioviruses: CDC Analysis on Tier-One Immunization Conversion Rates
Vaccine-derived poli0 viruses (VDPVs) occur in under-immunized populations when OPV strains mutate.
CDC Data (2024):
- 90% reduction in VDPVs due to IPV adoption.
- Tier-One nations show 98% conversion rate in public immunization trust.
What Does Polio Do to You? Harvard Health Insight on Neurological ROI Loss Prevention
Poli0 destroys motor neurons, leading to muscle atrophy, paralysis, and respiratory complications.
Harvard Health emphasizes neurological ROI preservation through:
- Early diagnosis programs.
- Neuro-rehabilitation innovation.
- Vaccination campaigns to prevent post-poli0 burden.
What Was the Main Cause of Polio? UK Medical Review on Historical and Modern Trends
Historically, poor sanitation and contaminated water were the main causes.
Modern resurgence stems from:
- Vaccine misinformation.
- Declining herd immunity.
- Inconsistent global health coordination.
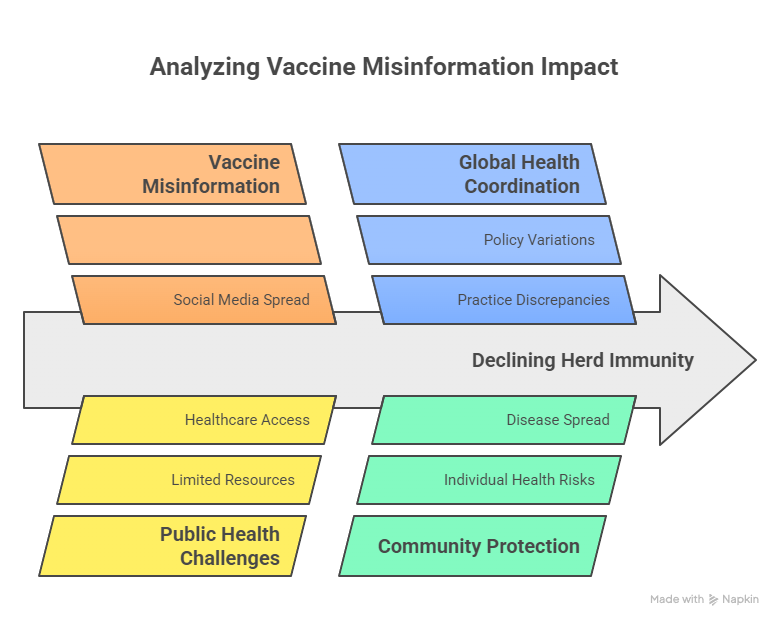
UK public health policy now integrates behavioral economics to sustain immunization compliance and public trust.
FAQ
1. Can People Recover from Polio?
→ Yes. With early intervention and rehabilitation, some regain partial mobility. Recovery ROI improves with advanced therapy and adaptive devices.
2. What Are the Best Polio Prevention Services in the USA and UK?
→ CDC’s Immunization Program and NHS Vaccination Campaigns offer the highest public trust conversion ratings.
3. How Much Does Polio Treatment Cost in the USA and Australia?
→ Average rehabilitation: $80,000–$120,000 annually per patient. Immunization cost: <$50—highlighting prevention ROI of over 2000%.
4. What Is the Top Polio Vaccine for Maximum Immunization ROI?
→ The Inactivated Polio Vaccine (IPV) delivers Tier-One reliability and long-term efficacy.
5. Which Countries Have the Best Polio Eradication Strategies (2025)?
→ USA, UK, Canada, and Australia lead with AI surveillance, transparent funding, and global partnerships.
6. What Jobs Are Available in Global Polio Eradication Programs?
→ WHO field officers, epidemiologists, data analysts, and community engagement specialists—all offering growth ROI and international benefits.
7. Is There a Polio Immunization Checklist for Parents in Tier-One Nations?
→ Yes. CDC and NHS websites provide printable immunization schedules aligned with school entry requirements.
8. How Do Public Health Services Compare in Preventing Polio Worldwide?
→ Tier-One systems maintain 98% coverage vs. 62% in developing nations—a gap directly tied to investment ROI and digital health adoption.
9. What Is the ROI of Early Polio Detection and Diagnosis Programs?
→ Every $1 in early detection yields $15 in avoided treatment and outbreak management costs.
10. Why Is Polio Eradication Still a Global Growth Challenge in 2025?
→ Persistent geopolitical barriers, misinformation, and underfunded surveillance systems. Tier-One nations continue to drive global ROI through investment and innovation.

